Introducing CT-001
A highly potent, safe FVIIa to treat uncontrollable fatal severe hemorrhage.
Why FVIIa?
FVIIa is required for clot formation to stop bleeding, and must be tightly regulated to prevent thrombo-embolic events.
-

Damaged Blood Vessel
Injury to vessel lining triggers the release of clotting factors.
-
Formation of Platelet Plug
Vasoconstriction limits blood flow and platelets form a sticky plug.
-

Development of Clot
Fibrin strands adhere to the plug to form an insoluble clot.

CT-001 is a novel FVlla variant with faster clearance and superior efficacy
Coagulation Cascade
The coagulation cascade is composed of a set of exquisitely controlled cofactors and proteases. At Coagulant, we are leveraging the full range of biological formats to mine this space to develop novel therapeutics to treat acute bleeds, the leading cause of death age 1-46.
CT-001 Demonstrates Superior Potency & Safety to rFVIIa in Multiple Murine Acute Bleeding Models
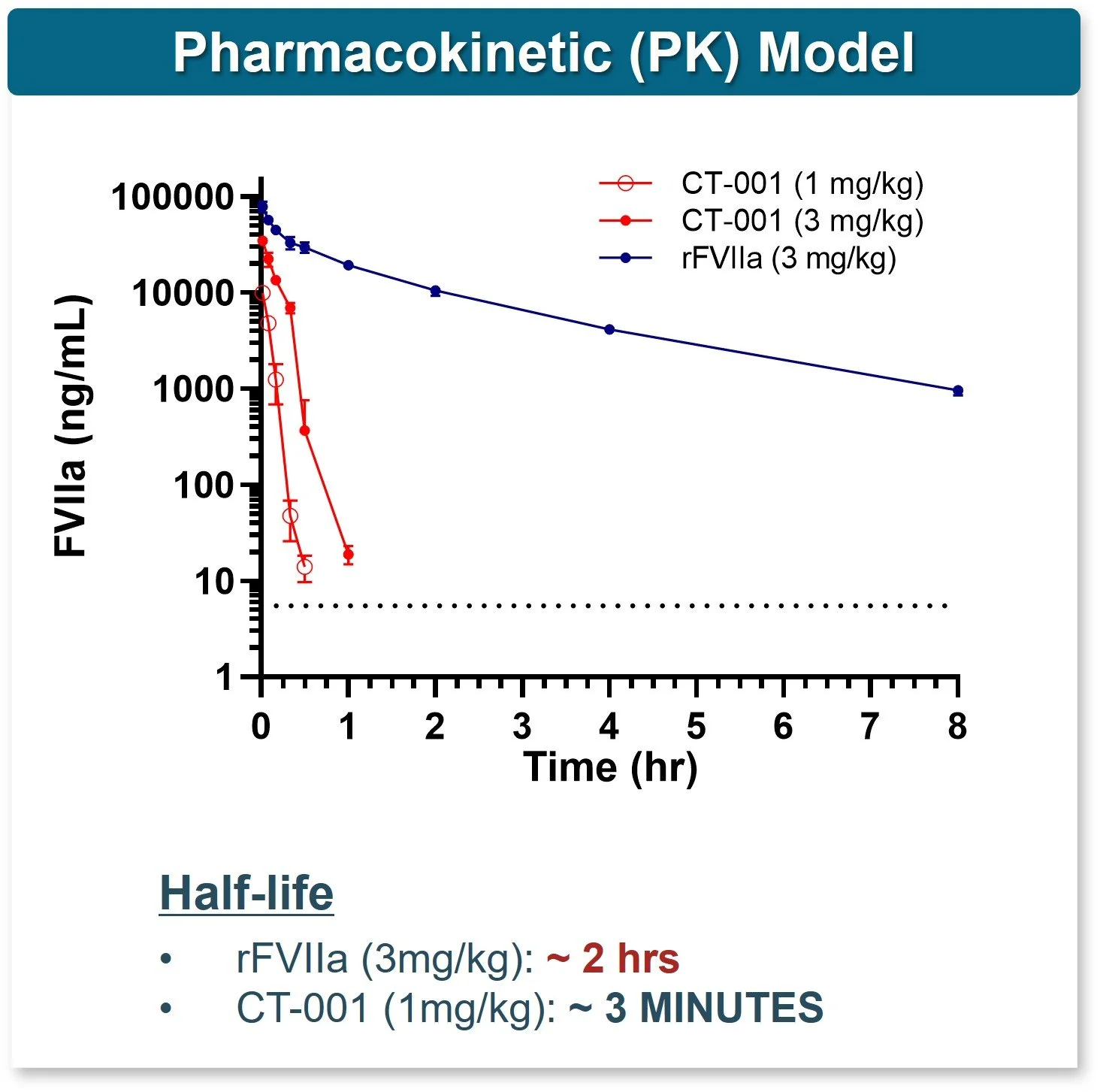
CT-001 is rapidly cleared
Decreased systemic exposure risk vs rFVIIa*
Consistent across mammalian species
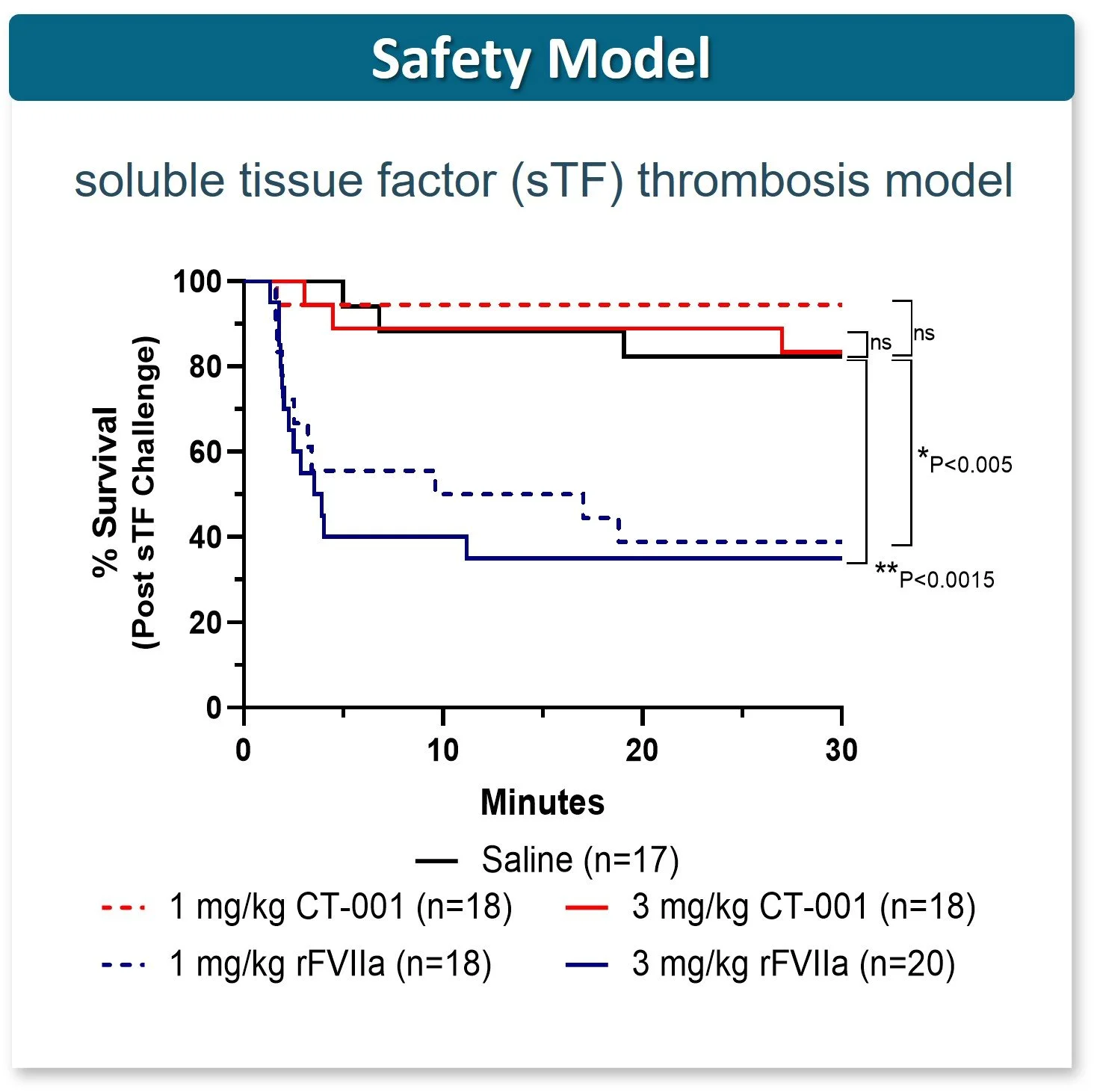
CT-001 Safety = Saline
CT-001 Safety > rFVlla
Similar favorable results in FeCl3- induced carotid artery thrombosis model
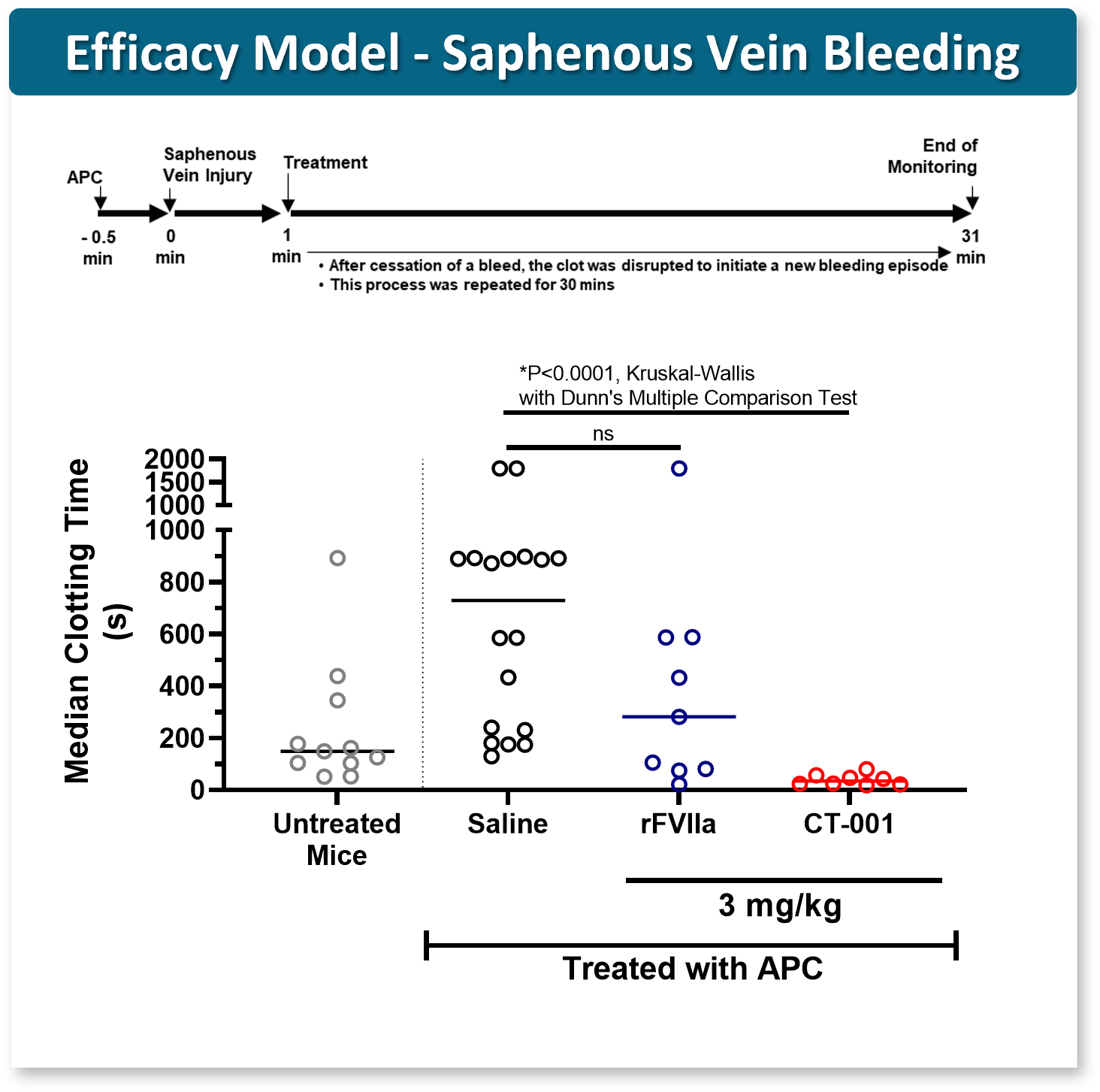
CT-001 highly efficacious
CT-001 potency > rFVIIa
Similar potency gains observed ex vivo with human PPH samples
Sim et al., Thromb Res 215: 58, 2022
*rFVIIa – recombinant Factor VIIa (NovoSeven®, eptacog alfa (activated))
CT-001 Provides Pro-Hemostatic Activity Under Coagulopathic Conditions
CT-001 corrected APTT of hypocoagulable plasma
CT-001 potency > rFVIIa*
CT-001 potency > rFVIIa
Sim et al., J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024, 96:276.
*rFVIIa – recombinant Factor VIIa (NovoSeven®, eptacog alfa (activated))
Introducing APC Program
Activated Protein C (APC) is an attractive target for treating acute bleeding
Developing APC-based therapeutics that selectively eliminate or retain APC functions individually, or in combination, has been challenging but would have significant impact across an array of diseases including trauma-induced coagulopathy, hemophilia, and sepsis.
Processes Modulated by APC
Trauma Induced Coagulopathy (TIC) is Mediated by Activated Protein C (APC)
TIC is associated with high mortality
Tissue endotheliopathy mediates the acute coagulopathy in trauma with APC being one of the contributing mechanisms
The targeting the APC pathway could help ameliorate bleeding, shock, and organ damage
Sepsis is a life threatening organ dysfuction and frequent common pathway to death from infectious diseases worldwide [1].
With high morbidity (est. 49M individuals) and mortality (11M deaths annually), it accounts for almost 20% of all global deaths [2].
A recent review suggest that an APC-based treatment has survival benefit and the Coagulant APC library represents an opportunity for a next generation APC-targeted treatment [3].
[1] Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA. The enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest 2003; 112: 460–67.
[2] Marshall JC. Why have clinical trials in sepsis failed? Trends Mol Med 2014; 20: 195–203.
[3] Famous KR, Delucchi K, Ware LB, et al. Acute respiratory distress syndrome subphenotypes respond di erently to randomized fluid management strategy. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2017; 195: 331–38.
Proprietary Nanobody Library – Unlocking APC Therapeutics
Challenges
Similarity between APC and Protein C - differ by 12 amino acids
Limited conformational differences upon activation
Solution
Llama Nanobodies
Small-sized antibodies (15 kDa)
Unique elongated shape
Longer average CDR3 than murine or human Abs
Allow targeting to inaccessible or 3D-structures not recognized by conventional Ab
Highly stable - liquid formulation suitable for battlefield and hospital use
Leveraging the unique properties of llama antibodies (referred to as nanobodies), we generated a proprietary novel nanobody library to APC.
By using assays specific for coagulation, inflammation signaling and histone cleavage functions of APC, we were able to identify an array of human APC specific antibodies able to retain or eliminate these functions.
This represents a tool chest for APC targeted therapies that has already identified a lead candidate for the treatment of trauma and hemophilia.
Sim et al., Blood Adv. 2023 Jul 11;7(13):3036-3048
CT-003 Lead Candidate Ameliorates Endotheliopathy by Preventing Vascular Endothelial Cell Layer Permeability
CT-003 lead candidate shifted PAR1 signaling towards anti-inflammation and cytoprotection
Sim et al., Blood Adv. 2023 Jul 11;7(13):3036-3048.
Publications
CT-001
In vitro characterization of CT-001-a short-acting factor VIIa with enhanced prohemostatic activity. Sim DS, Mallari CR, Teare JM, Feldman RI, Bauzon M, Hermiston TW. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2021 Jun 30;5(5):e12530.
CT-001 is a rapid clearing factor VIIa with enhanced clearance and hemostatic activity for the treatment of acute bleeding in non-hemophilia settings. Sim DS, Mallari CR, Teare JM, Bauzon M, Hermiston TW. Thromb Res. 2022 Jul;215:58-66.
Rapid clearing CT-001 restored hemostasis in mice with coagulopathy induced by activated protein C. Sim DS, Mallari CR, Bauzon M, Hermiston TW. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2024, 96:276.
CT-001, a novel fast-clearing factor VIIa, enhanced the hemostatic activity in postpartum samples. Sim DS, Mallari CR, Hermiston TW, Bae DK, Lee S, Allen T, Gilner J, Kim SC, James AH. Blood Adv 2024, 8:287.
CT-003/CT-005
Selective modulation of activated protein C activities by a nonactive site-targeting nanobody library. Sim DS, Shukla M, Mallari CR, Fernández JA, Xu X, Schneider D, Bauzon M, Hermiston TW, Mosnier LO. Blood Adv. 2023 Jul 11;7(13):3036-3048.
Divergent modulation of activated protein C pleiotropic functions by antibodies that differ by a single amino acid. Sim DS, Shukla M, Mallari CR, Fernández JA, Xu X, Schneider D, Bauzon M, Hermiston TW, Mosnier LO. Blood Adv. 2025 Jan 14;9(1):180-191.
Our Pipeline
We are developing landmark treatments in significant markets of unmet medical need starting with acute bleeding and extending into adjacencies such as acute care.
* TBD Phase 1 will be initiated with either CT-003 or CT-005, not both simultaneously

Contact us.
We are actively seeking for opportunities to collaborate with leading research institutions and biopharmaceutical companies to address unmet medical needs associated with the coagulation cascade.